The Task Manager in windows serves the fundamental purpose of overseeing all active processes on your computer. This makes it a crucial tool for users of all levels, whether you’re a beginner or an experienced system administrator.
With the Task Manager, you have the ability to forcibly terminate troublesome applications, deactivate lingering processes that remain after closing an app, observe background applications in operation, and gain insights into the present status of your system resources.
Given that the task manager is typically summoned when an application or process malfunctions, it’s prudent to acquaint yourself with multiple methods of accessing it. This way, you can avoid being stranded should a process impede your typical approach to reaching the task manager.
Table of Contents
What is Task Manager in Windows?
The Task Manager in Windows is a built-in system utility that provides users with a real-time view and management of the various processes, applications, and system resources running on their computer.
It offers insights into the performance of the computer and allows users to monitor, troubleshoot, and control running applications and background processes.
Functions of the Task Manager in Windows
Key functions of the Task Manager include:
- Process Monitoring: It displays a list of currently running processes, applications, and background tasks. Users can see information such as CPU and memory usage for each process.
- Application Management: Users can forcefully close or end unresponsive or misbehaving applications that might be causing issues.
- Resource Usage: The Task Manager shows the usage of system resources like CPU, memory, disk, and network. This can help users identify resource-hungry applications and potential performance bottlenecks.
- Startup Programs: It allows users to manage programs that start automatically when the computer boots up, helping to optimize startup times.
- Performance Monitoring: Users can view performance graphs that show how different system resources are being utilized over time.
- Users and Sessions: In systems with multiple user accounts, the Task Manager displays information about active user sessions and their associated processes.
- Services: It provides access to a list of system services, which are essential background processes that keep the operating system running smoothly.
- App History: Users can track resource usage over time for different applications.
- Details Tab: This tab provides more in-depth information about running processes, including their associated services, memory usage, and paths.
- Networking: Users can monitor network activity, including which processes are using the network and how much data they’re transferring.
- Users Tab: In professional editions of Windows, like Windows Server, this tab displays information about users currently logged in to the system.
10 Shortcut To Open Task Manager in Windows 10/11
Here are the best 10 shortcut to open task manager in windows.
1. Use the keyboard shortcut
The most convenient and swiftest approach to launch the Task Manager involves employing the dedicated keyboard shortcut. Simply press the combination of Ctrl+Shift+Esc keys simultaneously, and the Task Manager will promptly appear.
As long as your keyboard functions properly and there are no hindrances to using shortcuts, this technique should be your primary means of accessing the Task Manager.
2. Use Ctrl+Alt+Delete screen
Accessing the Task Manager is also achievable from the GINA screen, often referred to as the CTRL+Alt+Delete screen. Certain applications, particularly games, might impede your use of the Ctrl+Shift+Esc keyboard shortcut for launching the Task Manager. Nevertheless, CTRL+Alt+Delete remains effective, as it takes precedence over most processes.
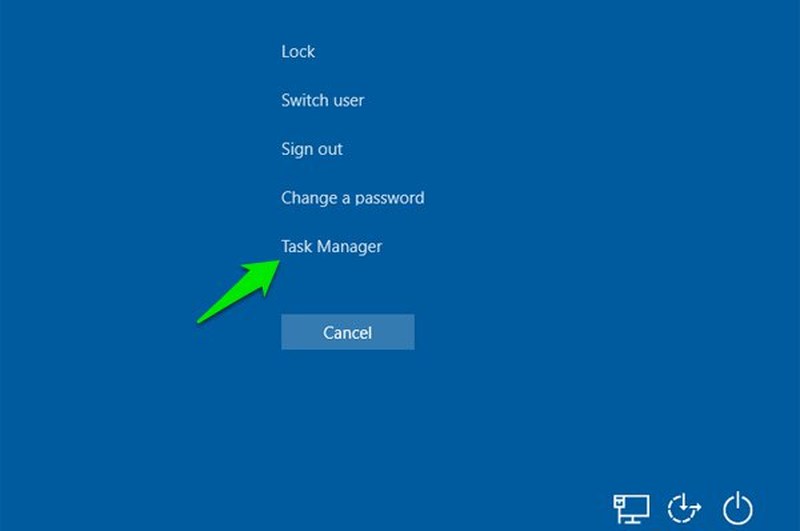
Simply press the Ctrl+Alt+Delete keys on your keyboard, and then select Task Manager from the list of choices that appears.
3. Use Windows Power User Menu
The Windows 10 power user menu incorporates an option for accessing the Task Manager. To do so, right-click on the Start menu button or press the combination of Windows+X keys. Once the power user menu appears, simply click on the Task Manager entry to launch it. This approach proves handy in situations where your keyboard is nonfunctional or when a mouse-based interaction is preferred.

4. Access from the taskbar menu
Much like the previously mentioned technique, there exists an avenue to reach the Task Manager through the taskbar menu. Right-click on an unoccupied area of the taskbar and opt for the Task Manager from the ensuing menu.
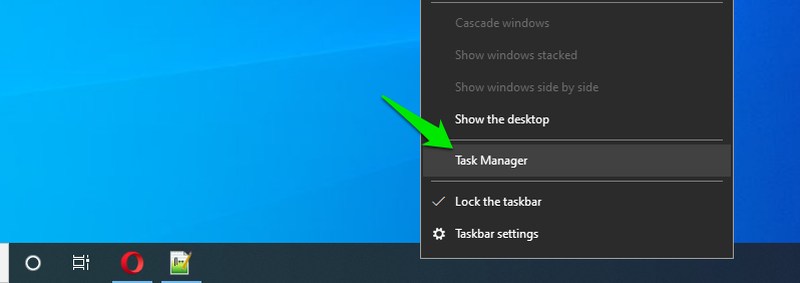
5. Run Command
A multitude of Run commands provide access to vital Windows components, including one designated for the Task Manager. To employ it, press the Windows+R keys to unveil the Run dialog. Within this dialog, input “taskmgr” and then select the OK button, triggering the Task Manager to open.

6. Run Task Manager executable
The Task Manager possesses an executable file akin to other installed applications. Therefore, you can locate this executable file within File Explorer and initiate it from there. Begin by launching This PC (or the applicable file manager tool). Navigate to the File Explorer and navigate to the following pathway: C > Windows > System32. Scroll through the contents and activate the executable file named “Taskmgr.”

Alternatively, you can directly access this location by entering “C:\Windows\System32\” into the search bar of the File Explorer. In the event that Windows is installed in a directory other than the C drive, navigate to the respective directory instead.
7. Use the Start menu
For those who favor launching applications through the Start menu, you can also access the Task Manager from there. Simply click on the Start menu and scroll to the bottom. From there, click on the Windows System folder, followed by selecting Task Manager within.

8. Pin Task Manager on the taskbar
For a swifter way to access the Task Manager using your mouse, you can integrate its executable into the taskbar, enabling one-click access. To achieve this, you’ll need to locate the Task Manager’s executable file, which can be accomplished using the aforementioned methods via File Explorer or the Start menu.

Upon locating the executable, right-click on it and choose “Pin to taskbar” to embed its icon into the taskbar. Like other icons on the taskbar, you can rearrange its position and initiate it with a single click. If you wish to remove it, simply right-click the taskbar icon and select “Unpin from taskbar.”
9. Use Control Panel
While navigating within the Control Panel, you can utilize its search functionality to reach the Task Manager. To initiate the Control Panel, you can either search for it using Windows search or utilize the Run dialog by typing “control” within it.
Once in the Control Panel, employ the search bar situated in the upper-right corner and input “Task Manager.” A compact link to the Task Manager will appear on the left side below the “System” section.
10. Use Command Prompt or Powershell
If you encounter a computer problem and require Command Prompt or PowerShell commands to resolve it, you can employ a command to access the Task Manager if necessary.
Both Command Prompt and PowerShell can be accessed via the Windows search bar. After launching one of these utilities, input “taskmgr” and hit Enter to open the Task Manager.
Conclusion
Mastering these taskbar shortcuts can significantly boost your productivity and make navigating through your open applications and features a breeze.
Whether you’re managing multiple virtual desktops or swiftly launching apps, these shortcuts will become invaluable tools in your Windows 10/11 experience. Remember, practice makes perfect, so don’t hesitate to integrate these shortcuts into your daily workflow and make the most of your taskbar’s potential.